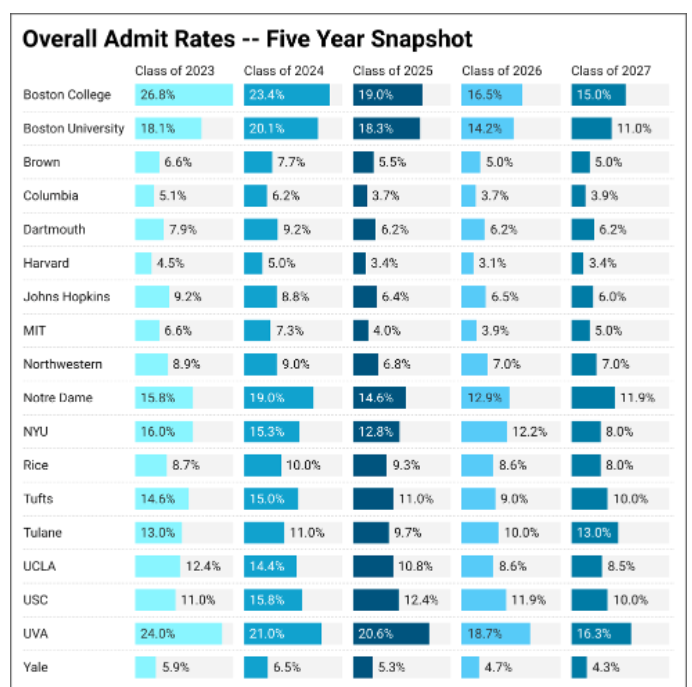
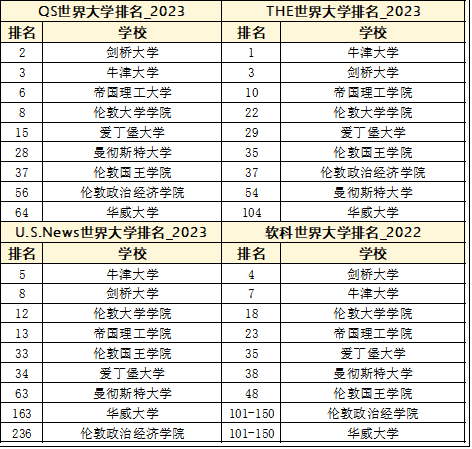
Hi,大家好,A Level 5月经济大考马上快开始了,根据新考纲规定,考生将必须从微观,宏观两个部分中分别选择一篇20分的essay完成,这就给一些考生带来了蛮大的压力,因为大家还是普遍认为宏观经济比微观经济要更难一些。不过没关系!今天学姐给大家整理了关于宏观经济的重要知识点汇总,希望能够帮到大家!
今天这篇文章所分享的内容基本上是Chapter 9的重点知识点和考点。第九章的内容之多,难点之多,我觉得是很有必要跟同学们好好总结总结的。其余的包括Chapter 10,11的知识点,相对于第九章来说,内容更少,更好理解,课本就能够涵盖所有的知识,在这里就不过多赘述了。
今天这篇文章将讲述一下4大知识板块的内容:
1. Money货币
2. Money supply 货币供给
3. Unemployment 失业率
4. Circular flow of income 收入的循环流动
大家可以根据自己的复习情况划到任意版块阅读。那么话不多说,一起来看看吧!
Money 货币
这一部分知识点主要以选择题的形式出现,大题出现的频率不高。我认为主要是需要记住money的定义,性质和功能。所以,我将这3点列出,并对特定学术词汇作出了详细的解释。
Money:
any items which can be used as a payment
Eg. Cash, deposit credit cards, debit card, gold, silver, bitcoin.
Functions of money:
1. Medium of exchange>>facilitate trade, promote specialization
2. Store of value>>saving, plan for the future
3. Unit of account/measure of value>>compare prices between different products
4. Standard of deferred payment>>credit(lending, borrowing)
基础名词(只需理解,非专门列出来的考点)
1. Deposit:银行账户里的存款。比如说你银行卡还有500元的余额,这个500就是你的deposit
2. Debit card &credit card的区别:debit card又叫借记卡,是只能存钱的银行卡,刷卡的时候最多只能够把你的deposit刷完。Credit card又叫信用卡,不光能存钱,还可以透支(overdraft)
3. Overdraft:透支的意思是,当你想要买的东西价格>银行存款时,你可以透支使用银行的钱,在下一次到期之前还款就行。至于能够透支花费多少,这得看你个人的信用有多少。
4. Notes纸币,coins硬币
5. Checks(cheques):支票,可以拿到银行去兑换对应金额的金钱。
Characteristics of money:
Portable
Generally acceptable
Recognizable
Identical
Divisible
Difficult to counterfeit
Scarcity
Money supply 货币供给
这一部分内容需要区分narrow money和broad money的不同点和各自的例子。中央银行和商业银行各自的职责,银行运作的规律也需要熟记。
Money supply:
total amount of money in an economy
Narrow money:
has strong liquidity, such as notes in circulation, cash held in banks (balance in checking/current account)and reserves held at commercial banks(till money)
Broad money:
narrow money+money used as a store of value
Eg. Shares, bills, bonds
Role of central banks:
1. Implement monetary policies
2. Banker of governments, commercial banks
3. Held foreign currency reserves
4. Monitor the banking system
5. Print money
Role of commercial banks:
1. Provide deposit account
2. Lending money:overdraft, loans
3. Holding or providing cash, securities, loans, deposits equity
银行是怎么赚钱的:
银行主要是通过利息差赚钱。比如说人们存钱的利息是2%,那么银行借出去的利息(用于investment)的就会到10%,银行赚取的就是中间8%的利息差。
Eg. Saving---banks---investments
Trade off between profitability and liquidity:如果银行想要赚取more profit,他就会多借钱出去;赚取更多的利息;但是同时bank里的reserves也会降低,如果存款人要withdraw存款,银行很有可能拿不出来;这就是我们所说的流动性降低。
Liquidity:how easy an asset can be converted in cash
Reserve ratio:准备金率(liquid ratio/cash ratio)
The minimum proportion of deposits that central banks requires banks and other financial institutions to hold, which is designed to satisfy withdrawal demand.
Reserve ratio & credit multipler:
如果reserve ratio=5%,cash一共是100 dollar。代表银行能够借出去95 dollar,这些钱如果都存进银行,银行又会借出去95x0.95,这样循环往复,银行所借出去的贷款的总额将会是1/reserve ratio=credit multiplier,也就是银行往经济体里注入的injection。
Government deficit financing:
如果government缺钱了,产生了budget deficit,那么就会发行债券来增加收入。
一共通过三种方式:
1. Central banks print money,将政府的bonds买下来,政府拥有了这笔钱了以后可以注入经济体。如果是central bank印钱的话,钱没有办法进入市场,因为central bank的钱本来在市场上就不流通,所以它通过政府,将这笔钱inject进市场。以上大概内容就是我们讲的量化宽松(QE)
2. Borrow from the commercial banks。政府将short-term bills卖给商业银行,银行将reserves给政府,政府拿到了钱;short-term bills的liquidity较强,因为一年之内政府就会返还钱+利息,所以二手市场非常愿意购买这些bills。所以,当银行需要借款的时候,他就会将bills卖给这些人,换取cash借给别人。这样子的话,银行依旧借钱,政府多了一笔钱,MS增加。
3. 第三种就是borrow from the private instututions/individuals。政府向老百姓借钱,老百姓为了买政府的bonds,会从银行取钱买,这个withdraw减少了银行可以借给investor的cash。所以,即使政府得到了钱,老百姓也失去了钱,MS不变。
Unemployment 失业率
失业率属于从G1开始就接触到的考点了。在A2的大纲中,大家需要知道失业率的衡量方法,造成原因和解决失业率的各种政策。
Unemployment定义:
people who are willing but unable to find a job
Working age population:16-65 yrs old; dependent population:小于16岁,大于65岁。
Working age population又可以分为两种,一种是economically active population,又称为labour force;一种是inactive population。
Economically active population可以分为employment和unemployment;inactive population就是那些不找工作/不愿意找工作/没有能力找工作的人,但是在working age里的人,比如说disabled;students;housewives;early retirements。
Dependency ratio=dependent population/working age population
Participation rate=labour force/working age population
Measurement of the unemployment:
claimant count:by counting the numbers of people who claiming for the unemployment benefits.
Labour force survey
Causes of unemployment:
Demand-side unemployment;
Supply side unemployment/natural rate of unemployment
Demand side unemployment:
Recession>>lower AD>>since labour is a derived demand>>loawer demand for labour
Reasons for natural rate of unemployment:
1. Frictional unemployment:arises when workers are between jobs;这种失业非常正常,分为search unemployment和casual unemployment:第一个是已经有了一份offer,但却不愿意去上班,想要更好的offer;第二种是自己的职业原因,有长短的休息时间,比如说actors,construction workers等等。
2. Seasonal unemployment:demand for workers fluctuates according to time of the year. eg.旅游业,每年有淡旺季之分
3. Real-wage unemployment:工资设置的太高,导致了surplus of labour,因为作为公司来讲,过高的工资导致对labour的需求量变小了,这也会导致失业。
4. Structural unemployment:refers to a type of unemployment that arises from the changes in the structure of the economy, it occurs when there is a mismatch of the skills and qualifications of workers and the available job opportunities.
5. Regional unemployment:when the declining industries are concentrated in a particular area of the country.
6. Factors affecting the natural rate of unemployment:
Minimum wage>>real-wage unemployment
Education and training>>structural unemployment
Wage differences between regions>>great icrentives for people to work in different area>>mobility increase>>natural rate of unemployment decrease
Cost of living in different regions>>geographical mobility decreases>>natural rate of unemployment increases
Policies to reduce natural rate of unemployment:
1. Education and training to reduce structural unemployment.
Eg. If the economy is shifting to the technology-based industries, those workers who have been trained will be in high demand. On the other hand, workers who lack these skills may struggle to find employment in the new economy, leading to structural unemployment.
2. Providing information to job vacancies>>reduce frictional unemployment
3. Provide infrastructure>>transport links>>reduce geographical unemployment
The difference between actual growth and potential growth:
Actual growth:an increase in real GDP
Potential growth:an increase in the quantity and quality of the FOP
Actural growth:
short run concept, either lower cost of production or increase the AD lead to the increase in real output. PPC图像上显示的是从内部一个点往外转移到线上。
Potential growth:
long run concept,PPC图像向歪shift,竖直的long run aggregate supply向外shift,或者在keynesian主张的aggregate supply中,图像往外shift。
Circular flow of income 收入的循环流动
这个部分是本章的核心知识点,考生需要掌握钱是如何在经济体里流动的,并学会用图表来说明。
For closed economy with no government:
we only have household and firm:
Household>>consumption of G&S>>firms
Firms>>income>>household
Investment>>injections inject to the firms
Household>>saving>>banks
With 3-sector economy, we add into the role of government:
Therefore, government spending(G) + taxation(S)is included.
AE=consumption+investment+government spending into the economy (AE=C+I+G)
With 4-sector economy, including the international trade:
The imports(M)and exports(X)are included
exports也相当于增加MS,所以也算进AE里面“+”
imports相当于钱流失到别的国家了,所以要减去“-”
overall, AE=C+I+G+(N-X)
injection-withdraw model:
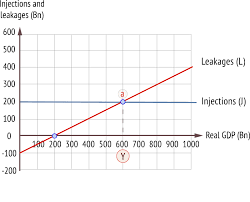
Why the injection line is horizontal?
因为injection的组成部分(政府开支government spending+投资investment+净出口net export)都与real GDP(总产量无关),因为这些都是government,bank,和international
Trade决定的。但是withdraw(是跟taxation,saving,imports有关的,这些都是根据output的增减发生变化的,因为income会发生变化,所以如果real GDP上升,leakage上升。
National income
National income is the value of total output produced by an economy over a period of time. People can earn an income from producing an output. The income is then spent on the output. This means that total output = total income =total expenditure.
好了!以上就是学姐总结的部分宏观经济的重点知识点。宏观经济的内容实在太多,涵盖的内容面太广,学姐建议大家复习的时候根据新的syllabus来复习,一个一个topic查看自己有没有遗漏的知识。
最后,AL国际考是A Level考生高中生涯的最后一门考试了。希望大家的A Level经济大考顺利!都能够过con美美进入大学学习~