昨天网上出现了今年印度卷的essay题,今天我们来对微观第一题进行详细的解析。
Q2(a)With the help of a demand and supply diagram, explain how the introduction of an indirect tax affects equilibrium in a market and consider the extent to which the incidence of the tax will fall on the consumer. [8]
AO1:解释indirect tax如何影响equilibrium.
这里由3部分组成。
1) 定义indirect tax,equilibrium
我个人的答题习惯:所有题目出现的可以定义的term我都会进行定义,避免不必要的丢分。
Mark scheme也许没有这么多定义的要求,然而考试并不是对着ms答题。
在不知道ms长啥样的情况下,纠结某个term需不需要定义不如多花半分钟进行一下定义,这不会对考试结果产生任何影响。
2)解释indirect tax如何影响supply curve
很多同学可能会写indirect tax增加cost of production,因此supply curve shift,这个理论上是不对的:indirect tax并不影响factor payments. 教科书上关于indirect tax影响supply curve是这么写的:

任何时候,你都要优先根据教科书内容来答题(除非书是错的)
3)解释equilibrium的变化 由于题目考的是tax incidence,在写market impact的时候,我会区分producer收的钱和consumer付的钱。
Sample
A market is in equilibrium when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. This is a balanced situation with no tendency to change, ceteris paribus. Indirect tax is levied on expenditures, such as sales tax and excise duties. Specific taxes are in the form of a fixed amount per unit purchased. When an indirect tax is imposed, this tax must be paid to the government by retailers, wholesalers, manufacturers and other providers of taxable goods and services. This means that a business requires a price that is higher than the original price by the amount of the tax. With a specific tax, this is represented by a shift to the left of the supply curve by the amount of the tax.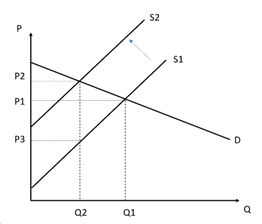
The price paid by consumers increases from P1 to P2 while price received by producers decreases from P1 to P3. Quantity demanded decreases from Q1 to Q2.
AO2+AO3:解释tax incidence. 这里也由3部分组成。
1)解释PED小于1的时候tax主要由consumer承担
2)解释PED大于1的时候tax主要由producer承担 由于教科书里关于tax incidence只写了PED,因此这里AO2部分我觉得并不需要讨论PES的影响。PES对tax incidence的影响可以放到AO3来写。 而题目没有出现PED这个词,答题的时候并不需要写PED相关的定义公式和解释。
3)evaluate到底是不是consumer承担,并给出conclusion
Sample
The incidence of a tax is used to describe the extent to which the tax burden is borne by the producer, by the consumer or by both. This depends on the value of price elasticity of demand (PED)
When demand is price-inelastic, it is easier for the seller to pass on the tax to the consumer in the form of higher prices. The burden of an indirect tax falls mainly on consumers.
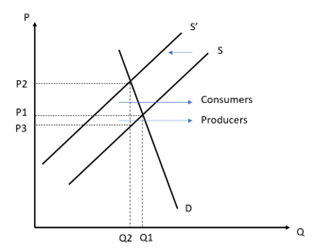
The burden on the consumer, which is equal to (P2 - P1) * Q2, is greater than the burden on the producer, which is equal to (P1 - P3) * Q2. When demand is price-elastic, consumers will invariably buy less of the product as price rises, resulting in the producer having to absorb a greater part of the indirect tax. In this case, the burden of an indirect tax falls mainly on producers.
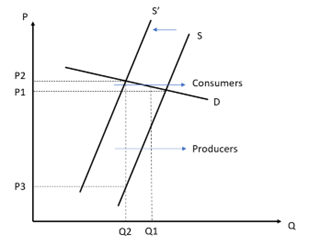
The burden on the consumer, which is equal to (P2 - P1) * Q2, is less than the burden on the producer, which is equal to (P1 - P3) * Q2. The incidence also depends on the price elasticity of supply (PES). Even if demand is price-inelastic, when supply is perfectly inelastic, the incidence of an indirect tax falls entirely upon the producers, as the imposition of an indirect tax does not increase the market price. Only when PED is less than PES, the indirect tax falls mainly on consumers. If PED is greater than PES, the indirect tax falls mainly on producers.
大家可能会发现,除了AO3之外,AO1和AO2的几乎所有内容我都是直接引用课本内容进行回答。 我知道大家很喜欢自己手里非教科书的学习资料,觉得教科书写的一坨答辩,但是我再强调一下:
参加新考纲的考试,教科书是最好的应试资料。
(b) Assess whether the improved provision of information is likely to be the best method to reduce the consumption of demerit good. [12]
AO1: 解释demerit good AO1最多只有2分,大家只需要给出解释+例子就好了。
A demerit good is seen as any product that is thought to be undesirable and which is overprovided by the market. Cigarette is a demerit good because consumers are unaware of its harmful effects, such as cancer and heart disease.
需要注意的是,这里的例子需要和后面的policies保持一致。 而大家可能都比较习惯香烟对应的policies,因此这里用香烟举例是最合适的。
AO2:improved information为什么可以/不可以减少consumption 如何减少consumption,需要详细写出provision of information的具体内容(例如通过公益广告告诉消费者香烟的危害),然后再去写对应的market impact. provision的问题,可以写很难改变消费者的习惯,消费者由于知识有限无法理解危害性。这里一定要围绕不能减少consumption来写,而不是诸如government spending有opportunity cost之类的general的问题。 这里可以/不可以对应的分数是一样的,每一边都要做到详细解释。
AO2:indirect tax为什么可以/不可以减少consumption
由于a问已经写了market impact,这里不用重复描述。可以提到high tax rate可以减少Q,并且由于incentive的问题Q总是能减少一些。
indirect tax的问题,可以写inelastic demand,以及black market.这里同样需要围绕consumption来写,不能写general problems.
AO3:讨论哪个policy是最好的
这里题目问的是best,而不是effectiveness,因此可以写的点有很多,包括但不限于:
1) indirect tax提供tax revenue,可以用来fundinformation provision. 因此sr用indirect tax, lr用information provision.
2) indirect tax的结果可以从市场数据来分析,如果Q没有减少那就增加tax rate;而information provision如果不成功gov无法改善policy.
3)indirect tax可以作为information provision的一部分(consumer发现一个商品加了很高的税会意识到这个商品一定是不好的),因此gov不用额外使用provision这个policy
4) indirect tax提高了市场价格,虽然减少了Q但是对穷人不利;一个高价会让consumer误以为这个商品有benefits从而继续购买。Information provision解决根源问题,并且让香烟的价格正确反应他的价值。
篇幅原因,这里我就不写sample了,希望以上的内容可以帮助大家进行完整答题。
微观的第二题非常简单,这里我也不再进行详细解释了,大家有时间可以拿来练练手,看看能不能在40分钟内写完。
考试的时候不仅要会写,写完也是很重要的。大家不要忽略了熟练度的练习。
3 (a) With the help of a formula, explain the meaning of income elasticity of demand and consider the extent to which a rise in income will increase the consumption of all goods and service. [8]
(b) Assess whether an estimate of the price elasticity of demand for a product is likely to be more useful to a firm than an estimate of its price elasticity of supply. [12]
以上就是今天的内容,祝大家学习顺利~