IGCSE Chemistry
今天为大家分享CAIE IGCSE化学酸碱盐(Acids, bases and salts)部分笔记总结。
Properties of Acids
- An acid is a compound which when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions (H + ) and are described as proton donors (H + )
- Acids turn blue litmus indicator paper (or solution) red.
- Have pH 1 to 6
- Acid + metal → salt + hydrogen gas
- Acid + base → salt + water
- Acid + metal carbonate → salt + carbon dioxide + water
- Strong acids completely ionize in water producing lots of H+ions
- Weak acids partially ionize in water producing few H+ions
Properties of Bases
- Bases are insoluble substances which neutralize acids to form a salt and water only and are proton acceptors
- Alkalis turn red litmus indicator paper (or solution) to blue.
- Have pH 8 to 14.
- Base + acid → salt + water (+ CO2 when base is a metal carbonate)
- Base + ammonium salt → salt + ammonia gas + water
- Strong alkalis completely ionize in water producing lots of OH-ions
- Weak alkalis partially ionize in water producing OH-ions
Neutral
- Neutral substances are pH 7.
- Acidity in soil:
Plants grow at a pH near 7.
-
If it is too acidic or alkaline they will not grow. Acidic soil is fixed by adding lime.
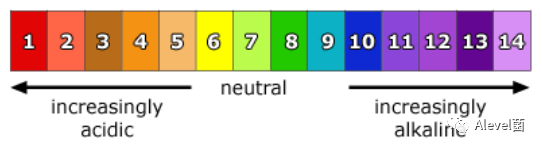
- pH is the concentration of H+ions per dm3 of solution
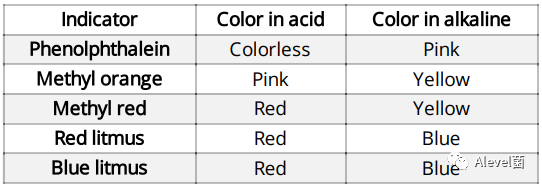
Indicators
Types of Oxides
- Metal oxides are basic e.g. iron oxide and magnesium oxide
- Non-metal oxides are acidic e.g. sulphur oxide and carbon dioxide
- Aluminum, zinc and lead form amphoteric oxides e.g. zinc oxide
- Oxides which are neither acidic or basic are neutral e.g. water and carbon monoxide
Preparation of Salts
- A salt is a substance formed when all the replaceable hydrogen ions of an acid are replaced by metal ions or the ammonium ion
-
Salts can either be soluble or insoluble
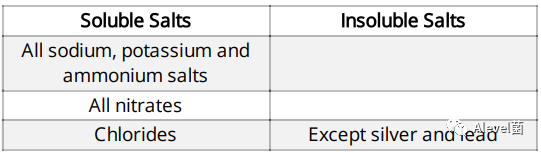
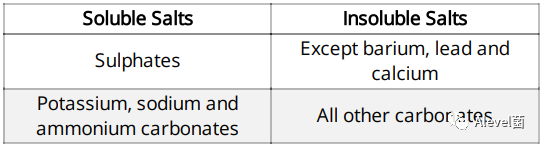
Type of Salts
| Type of Salt Required |
Acid used |
| Sulphate | Sulphuric acid |
| Nitrate | Nitric acid |
| Chloride | Hydrochloric acid |
| Ethanoate | Ethanoic acid |
Starting with a Metal
- Add excess metal to an acid
- When bubbling (hydrogen) stops the reaction is done
- Filter off excess metal
Starting with an Insoluble Base
- Add insoluble base to acid and heat gently, it will dissolve
- Keep adding until no more dissolves (reaction is done)
- Filter out the insoluble (excess) base
Starting with an Alkali (Titration)
- Put a certain amount alkali in a flask
- Add phenolphthalein
- Add acid from a burette, stirring, until it goes colorless
- Find out how much acid you used
- Repeat, to be more accurate
- Evaporate water from neutral solution
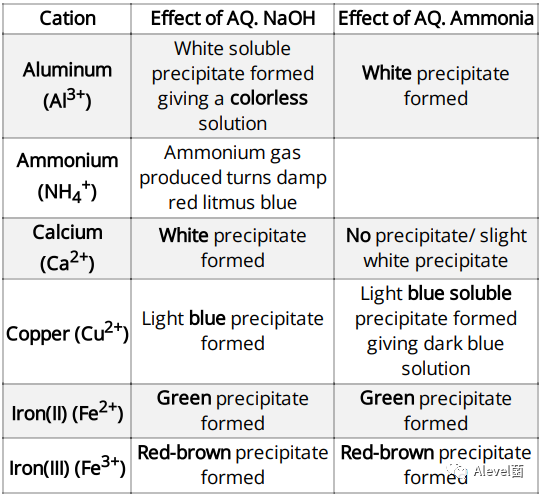
Test for Aqueous Cations

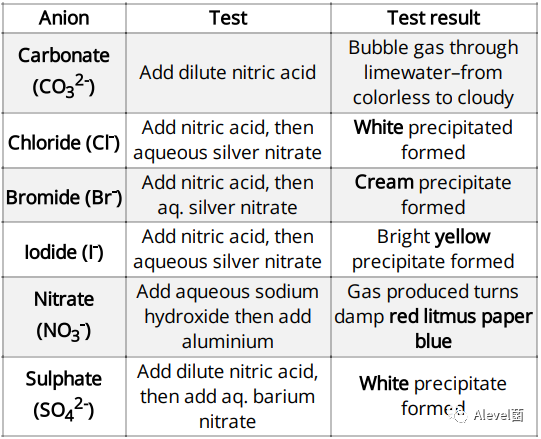
Test for Anions
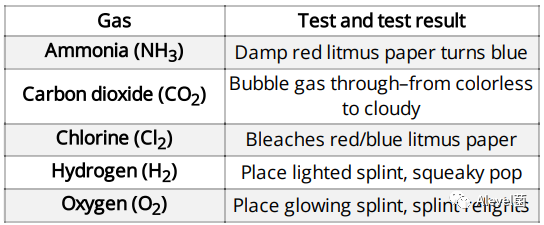
Test for Gases