观点类大作文,文化类话题
Historical objects in museums all over the world should be returned to their country of origin. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
题目来源:2024年9月28日大陆雅思大作文
1、题目大意
世界各地博物馆的历史文物都应该归还给原来的国家。你在多大程度上同意或不同意?
2、思路解析
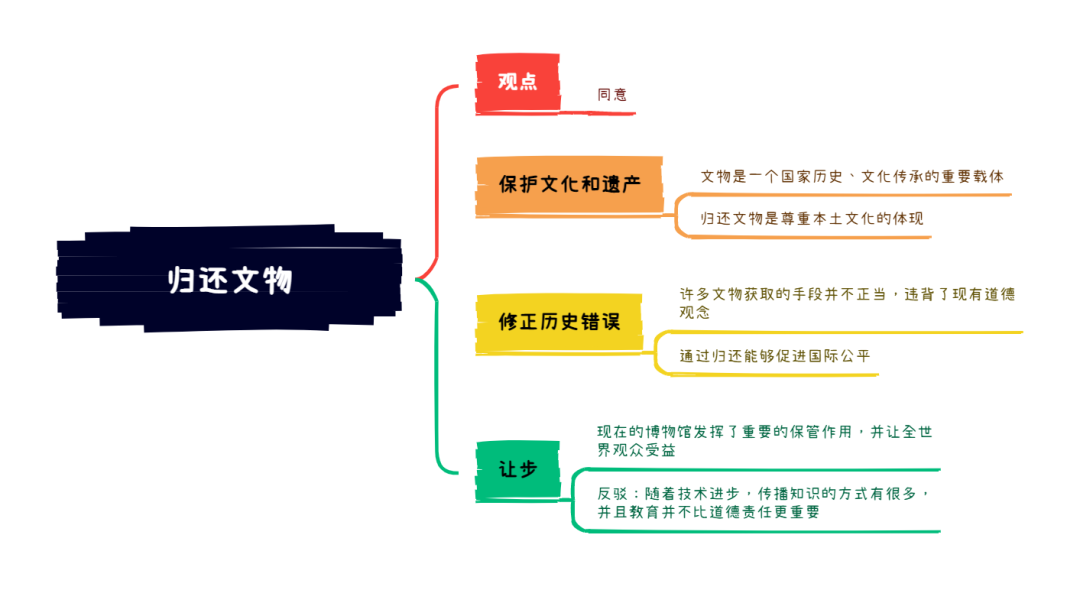
这是一道观点类大作文,聊的是归还文物的话题。题目难度较大,文化类相关的内容相对来说都比较抽象,对同学们的语料积累是一个考验。题目本身正反观点都可以写,甚至持不同意角度还会更好写一些,不过作为中国人,大家肯定希望流失在外的文物都能尽快回国,所以下面的观点我们会像以往一样列下正反观点,而范文会展示给大家如何贴脸开大。
首先来看反对角度观点,一般来说两个。
一是归还可能不利于部分文物的保护。一些原产国可能缺乏足够的资源、技术和专业知识来妥善保存和展示文物,导致其可能面临损坏、盗窃或毁坏的风险。而国际知名博物馆通常拥有先进的保护设施和专业团队,能够确保文物得到最佳的维护和安全保障,从而延长其寿命。
二是有些文物是通过合法途径获得的,符合当时的法律和国际协议,比如由原产国主动赠与。强制归还这些文物可能违反现有的法律原则,造成法律纠纷。此外,这可能会导致大量的索赔请求,给博物馆和政府带来复杂的法律和财政问题,影响文化机构的正常运作。
再来看支持将文物归还原产国,有三方面。
一是将历史文物归还原产国有助于保护该国的文化遗产,增强人民的民族认同感。文物是一个国家历史和文化的象征,承载着独特的文化内涵。通过归还文物,原产国人民可以更全面地了解自己的历史和传统,从而促进文化传承和教育。这对于保持文化多样性和丰富人类文明具有重要意义。
二是许多文物是在殖民时期、战争或非法交易中被掠夺或获取的。归还这些文物是对历史不公的纠正,体现了对原产国主权和文化遗产的尊重。这种做法符合国际道德准则,有助于修复历史创伤,促进国际正义和公平得以实现。
三是文物归还可以加强国家之间的外交关系,促进文化交流与合作。通过归还文物,持有国表达了善意和尊重,有助于改善双边关系。这不仅有利于政治和经济合作,还能促进学术研究和文化项目的共同开展,增进各国人民之间的理解和友谊。
3、提纲
4、高分范文示例
In an increasingly interconnected world, the possession and display of historical artefacts have sparked significant ethical debates. The question of whether such objects should be returned to their countries of origin has gained momentum as nations seek to reclaim their cultural heritage. I fully agree that historical items housed in foreign museums should be repatriated to their rightful homelands.
Firstly, returning artefacts is crucial for preserving the cultural identity and heritage of originating countries. These objects are not merely relics; they are tangible connections to a nation's history, traditions, and ancestral narratives. When artefacts remain abroad, the originating culture is deprived of essential components that contribute to its historical continuity and national pride. For example, the Elgin Marbles, taken from Greece and housed in the British Museum, are integral to Greek heritage and their absence diminishes the cultural landscape of Greece itself. By repatriating such items, we acknowledge and respect the intrinsic value these objects hold for their native societies, thereby strengthening global cultural diversity.
Secondly, many historical objects were acquired under questionable circumstances, often during periods of colonization or conflict. Retaining these artefacts perpetuates the injustices of the past and undermines ethical standards in the present. Repatriation serves as a form of restitution, addressing historical wrongs and promoting international goodwill. For instance, numerous African nations have called for the return of artefacts taken during colonial rule, viewing their retention as a lingering symbol of oppression. By returning these items, museums and governments can actively participate in healing historical wounds and fostering more equitable international relationships.
Admittedly, some argue that international museums provide broader access to historical artefacts, offering educational benefits to a global audience. They contend that these institutions serve as custodians, preserving artefacts for humanity at large. However, with advancements in technology, digital exhibitions and high-quality replicas can disseminate knowledge without depriving originating countries of their heritage. Therefore, while the educational role of museums is important, it does not outweigh the ethical imperative to return artefacts to their rightful owners.
In conclusion, the repatriation of historical objects is essential for preserving cultural identities and rectifying past injustices. While global access to history is valuable, it should not come at the expense of a nation's right to its own heritage. Returning artefacts to their countries of origin is a crucial step toward promoting ethical stewardship and global cultural respect.
5、相关词汇和语法结构
Increasingly interconnected world日益互联的世界
Possession and display of historical artifacts历史文物的占有和展示
Sparked significant ethical debates引发重大伦理辩论
Gained momentum获得动力
Reclaim their cultural heritage收复他们的文化遗产
Housed in foreign museums收藏在外国博物馆
Preserving the cultural identity and heritage保护文化身份和遗产
Tangible connections to a nation's history与一个国家历史的有形联系
Deprived of essential components被剥夺了重要组成部分
National pride 民族自豪感
Integral to 对……至关重要
Diminishes the cultural landscape削弱了文化景观
Acknowledge and respect the intrinsic value承认和尊重内在价值
Strengthening global cultural diversity加强全球文化多样性
Acquired under questionable circumstances在可疑情况下获得
Perpetuates the injustices of the past延续了过去的不公正
Undermines ethical standards削弱道德标准
Serves as a form of restitution作为一种补偿形式
Healing historical wounds治愈历史伤痛