双边类大作文,环境类话题
Some people argue that the companies and private individuals should pay the bill of cleaning up the pollution they produced, while others believe that it is the government's responsibility. Discuss both views and give your own opinion.
题目来源:2009年7月11日大陆雅思大作文
1、题目大意
一些人认为企业和个人应该为清理他们产生的污染买单,而另一些人则认为这是政府的责任。讨论两种观点并给出你自己的看法。
2、思路解析
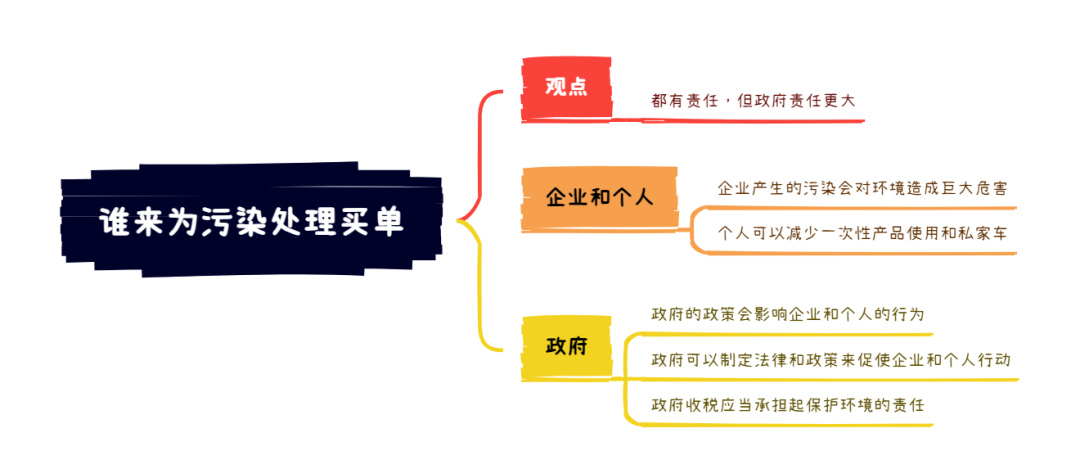
这是一道双边类大作文,聊的是污染谁买单的问题。双边类大作文,需要对每个观点分别表达同意或反对,最终的结论就是我的立场,可以是中立(双方都同意或都反对),也可以是单边支持某一方立场。题目理解上不难,非常经典的政府、企业和个人三方的责任义务讨论,在论证时都需要提及,下面,王珍老师和大家一起来看下具体观点。
首先来看前者观点的合理性,即企业和个人需要为污染负责。
一方面,公司和个人都有责任保护我们共同居住的环境。污染不仅对环境造成长期损害,还会影响人类健康、生物多样性和整体生态系统的平衡。因此,造成污染的公司和个人有责任采取措施减轻和清理他们造成的污染,以减少对他人的负面影响。
另一方面,强制污染者承担清理成本也是一种促进手段。这种“付费模式”可以促使公司和个人在其经营和生活中采取更可持续的方法,激励公司采用更清洁的技术和方法,降低自身后续治理费用成本的同时,也能够减少环境影响。
再来看后者观点的合理性,有三方面。
一是相比于个人或企业,政府通常拥有更多资源和能力,比如资金、技术和人力,来进行污染清理和环境保护。同时,在全球性环境污染问题上,需要各国政府达成合作共同采取行动。
二是政府应当制定环境保护法律和政策,并监管这些政策的实施。如果只是想清理的任务交由个人或公司来完成,很难确保最终的成效。资源不足的个人或小公司无法承担清理费用,而大公司则可能利用其资源和影响力逃避责任。
三是环境保护关系到居民的公共利益,政府在收取税款的同时应当承担相应的责任,包括保护其公民不受环境污染的危害,并维护空气、水和土地的质量。
3、提纲
4、高分范文示例
The rampant environmental degradation, an unfortunate by-product of anthropogenic activities, is becoming a poignant concern that significantly affects the tapestry of human life. This raises a contentious debate regarding the primary agents responsible for this ecological despoliation. Is it the ordinary citizens, the industrial entities, or the government itself? I posit that while humanity at large, being inhabitants of this planet, bear a portion of the responsibility, it is primarily the mantle of the government to shoulder the fiscal and policy-making burden for rectifying this environmental crisis.
Indeed, the average individual's eco-footprint is rarely enough to induce irreparable harm to our environment. Yet, the cumulative pollution arising from myriad commonplace activities such as petrol combustion or the prolific use of disposable products is undeniably significant, given our vast population. The pollution generated by industrial entities, however, is far more severe. Take, for instance, the atmospheric toxicity resulting from industrial exhaust emissions, which not only contribute to ozone depletion and climate change, but also disperse harmful substances that jeopardize human health. Moreover, the effluent discharge from chemical factories can cause persistent soil contamination, wreaking long-lasting havoc on the ecosystem. Hence, both citizens and corporations must acknowledge their role in this ecological crisis and take meaningful steps towards mitigation. Individuals could minimize the use of disposable products, while industries should prioritize waste treatment before discharge.
Nevertheless, we cannot exclusively fault individuals and corporations for this predicament. An under-emphasized and often overlooked catalyst for both domestic and industrial pollution is the governmental permitting process. Typically, neither individuals nor corporations possess the ability to comprehend the aggregate implications of pollution. Thus, the onus falls on the government, with its regulatory capacity, to orchestrate a harmonious balance between environmental conservation and economic progress. When governments prioritise GDP growth over environmental protection or exhibit laxity in pollution control policies, it is unjust to expect citizens to foot the bill. Without legal and policy restrictions, the motivation for environmental protection amongst corporations and individuals will likely be minimal. Furthermore, insufficient government support can hamper efforts to foster a greener lifestyle. For example, without a well-developed public transport system facilitated by the government, it is unrealistic to expect people to abandon private vehicles. Additionally, the public has already contributed tax dollars earmarked for regulatory actions, including pollution mitigation.
To encapsulate, it is essential to note that while individuals and corporations play a part, the primary responsibility for combating environmental pollution rests squarely on the shoulders of the government.
5、相关词汇和语法结构
Rampant environmental degradation 肆虐的环境退化
Anthropogenic activities 人类活动
Poignant concern 深切关切
Contentious debate 有争议的辩论
Eco-footprint 生态足迹
Irreparable harm 无法修复的伤害
Cumulative pollution 累积污染
Prolific use of disposable products 大量使用一次性产品
Atmospheric toxicity 大气毒性
Ozone depletion 臭氧层损耗
Persistent soil contamination 持续的土壤污染
Under-emphasized and often overlooked catalyst 被低估和经常被忽视的催化剂
Aggregate implications of pollution 污染的总体影响
Orchestrating a harmonious balance 协调和谐的平衡
Laxity in pollution control policies 污染控制政策的松散
Foot the bill 买单
Foster a greener lifestyle 培养更绿色的生活方式
Rests squarely on the shoulders of 完全落在...的肩上