随着新年的钟声渐渐响起,全球辩手们的心跳也在同步加速。2025冬季赛事的辩题,终于在千呼万唤中揭晓啦~
想象一下,站在世界级的辩论舞台上,面对来自世界各地的顶尖对手,你准备好迎接这场智力与口才的较量了吗?2025年的开端之战即将拉开帷幕。
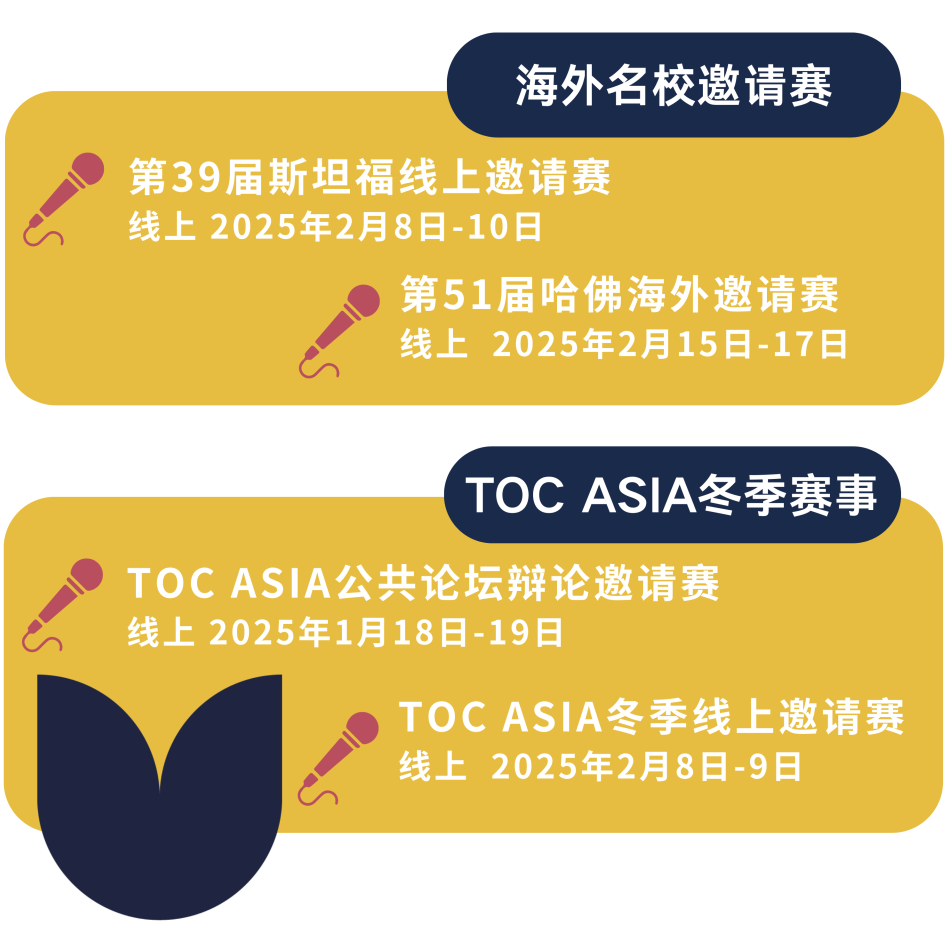
❗❗TOC ASIA 2025冬季赛事与哈佛/斯坦福年度邀请赛采用同一辩题。
今日,我们将揭晓关于2025冬季公共论坛辩论&小学生辩论备稿辩题两大重要信息,包括辩题公布及Sample Case的提供。

01冬季赛辩题
2025 WINTER
公共论坛辩论辩题
Public Forum Debate
Resolved: The United States should accede to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court.
美国应加入《国际刑事法院罗马规约》。
小学生辩论备稿辩题
Junior Debate
1、Topic
We believe that there should only be one host city for all the succeeding Olympics instead of electing different host cities for each Olympics.
我们认为所有未来的奥运会都应由一个固定的主办城市举办,而不是为每届奥运会选举不同的主办城市。
Info slide: The host of the Olympics is elected by the members of the International Olympic Commission (IOC) through a secret ballot from the countries that submit their bids. Different countries bid for different Olympics. For example, Paris was elected as the host city for the 2024 Summer Olympics last 2017 while Milan and Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy was selected to host the 2026 Winter Olympics last 2019.
2、Topic
We prefer a world where people can foresee the consequences of their actions.
我们更倾向于一个人们能够预见自己行为后果的世界。
3、Topic
We support the rise of AI chatbots.
我们支持人工智能聊天机器人的崛起。
4、Topic
We support the implementation of the Universal Basic Income in developing countries.
我们支持在发展中国家实施全民基本收入政策。
Info Slide:The Universal Basic Income (UBI) is a financial system where all individuals receive a regular, unconditional sum of money from the government, regardless of their circumstances or employment status. The goal of UBI is to provide a safety net that ensures everyone can meet their basic needs, reducing poverty and inequality.
JD备稿辩题·使用规则
Junior Debate
在冬季邀请赛小学生辩论中,如果预选赛轮数达到7轮或以上(如在Round Robin赛制中可能出现的情况),我们将依照顺序使用上述四个辩题进行比赛。若预选赛仅有5轮,那么第四个辩题将被安排在淘汰赛的第二轮中使用。
02Sample Case
2025 WINTER
距离冬季邀请赛仅有一个月时间啦!在此,我们将奉上由TOC ASIA学术总监Will教练精心准备的“Sample Case”,助力选手们迅速掌握辩题的核心,激发他们的思考,提升备赛效率。我们期待每一位辩手都能“吃透辩题,勤勉以赴”,因为只有深入理解辩题,才能在辩论中游刃有余,展现出最佳的自我。


Resolved
The United States should accede to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court.
Sample Pro Case
We affirm the topic: Resolved: The United States should accede to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC).
Contention 1: Accession Enhances International Accountability
Currently, the ICC serves as the world’s primary institution for prosecuting heinous crimes. However, its legitimacy is undermined by the absence of major powers, including the United States, whose non-membership weakens its ability to enforce justice effectively.
By acceding to the ICC, the U.S. would provide a much-needed endorsement of the court’s mission. U.S. participation would strengthen the ICC’s enforcement mechanisms by providing critical resources, including financial contributions and operational support for investigations.
Strengthening the ICC ensures that perpetrators of crimes like genocide and war crimes are held accountable. For instance, successful prosecutions of high-profile criminals such as Thomas Lubanga (a Congolese warlord) demonstrate the ICC’s potential when supported by its member states. U.S. accession would enhance this capacity, reducing impunity and deterring future atrocities, saving lives and promoting global stability.
Contention 2: Strengthening Multilateral Cooperation in Justice
The international justice system lacks coordination because not all nations are party to the ICC. This fragmentation hinders effective prosecution of cross-border crimes. For example, the inability to fully prosecute crimes committed during the Darfur genocide in Sudan illustrates the challenges of fragmented systems, as Sudan is not a party to the Rome Statute and international cooperation has been inconsistent.
By acceding to the Rome Statute, the U.S. would strengthen multilateral cooperation and coordination among states. The U.S. could work with other ICC member states to address crimes in regions like Darfur, where international efforts are currently fragmented due to jurisdictional issues.
Improved coordination creates a unified front against impunity for heinous crimes, increasing efficiency and effectiveness in prosecuting international criminals. This not only promotes justice but also reinforces stability in regions affected by conflict and mass violence, advancing the framework of global justice.
Contention 3: Accession Addresses Accountability Gaps in U.S. Law
The U.S. legal system does not always provide mechanisms to prosecute individuals for international crimes committed abroad. For example, war crimes committed by non-state actors or in unregulated jurisdictions often go unpunished because of limited extraterritorial jurisdiction in U.S. courts.
The ICC serves as a complementary institution, stepping in only when national courts are "unwilling or unable" to act. U.S. membership would not replace domestic mechanisms but instead fill accountability gaps by ensuring that perpetrators of war crimes, crimes against humanity, and genocide are brought to justice.
Victims of international crimes deserve justice, and U.S. accession to the ICC reinforces the principle that no one is above the law. Ensuring accountability deters future atrocities and strengthens both U.S. and global legal systems.
Sample Con Case
We negate the topic: Resolved: The United States should accede to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC).
Contention 1: The ICC’s Inefficiencies Undermine Justice
The ICC has been criticized for inefficiency, as demonstrated by its low conviction rate—only 10 convictions in over 20 years—and delays in prosecutions. For example, the case against former Ivory Coast President Laurent Gbagbo took over eight years and resulted in acquittal due to insufficient evidence.
U.S. membership would further strain the ICC’s limited resources, as new cases involving U.S. nationals or actions would demand additional attention. This diverts resources from pressing cases in developing nations, where atrocities are ongoing.
A weaker, overburdened ICC delays justice for victims and reduces the deterrent effect of international accountability. Instead of improving the ICC, U.S. accession would exacerbate its inefficiencies and harm its ability to prosecute the world’s most heinous crimes.
Contention 2: The ICC’s Overlapping Jurisdictions Create Legal Confusion
The ICC operates under the principle of complementarity, meaning it only acts when national courts are "unwilling or unable" to prosecute. However, this vague standard often leads to disputes over whether a case should fall under ICC or domestic jurisdiction, as seen in past investigations involving member states.
U.S. accession to the ICC would introduce similar jurisdictional conflicts, particularly in complex cases involving multinational actors or overlapping legal systems. These conflicts could delay justice, as parties dispute whether the ICC or U.S. courts should have authority over a given case.
Legal confusion undermines the efficiency and predictability of justice systems, frustrating victims and weakening public confidence in both domestic and international courts. Ensuring clear jurisdictional boundaries allows the U.S. to address international crimes more decisively without risking delays caused by disputes over authority.
Contention 3: Accession Risks Harm to Private Citizens and Organizations
Currently, U.S. citizens, NGOs, and corporations operate under domestic legal protections. These protections ensure accountability while minimizing exposure to differing international standards.
Accession to the ICC would subject U.S. citizens and organizations to international investigations, even for actions taken in good faith. The ICC’s jurisdiction over member states’ nationals and territories creates risks for humanitarian workers, businesses, and individuals operating in conflict zones.
The threat of ICC investigations could discourage U.S. organizations from engaging in vital humanitarian efforts in regions of ICC interest. This chilling effect would harm vulnerable populations reliant on these services and undermine global stability.

Topic1
We believe that there should only be one host city for all the succeeding Olympics instead of electing different host cities for each Olympics.
Sample Pro Case
1. Cost Efficiency for Long-Term Investment
Hosting the Olympics requires building large-scale infrastructure like stadiums, Olympic villages, and transportation systems. A permanent host city can focus on maintaining and improving these facilities over time, eliminating the need for massive investments every four years. For example, Rio de Janeiro spent $13 billion on the 2016 Olympics, and much of its infrastructure is now underutilized. By centralizing the Olympics in one city, resources can be allocated more efficiently, benefiting the athletes and spectators while reducing waste. The magnitude of cost savings is enormous, and the risk of host cities going into debt, as seen in Athens in 2004, is drastically reduced. This ensures long-term stability for the Olympics.
2. Environmental Sustainability
Different host cities often engage in extensive construction projects that harm the environment. Clearing land, building venues, and constructing transportation networks can lead to deforestation, pollution, and waste. A single host city can focus on sustainability, using existing facilities and reducing the environmental footprint of hosting the Games. For instance, the carbon emissions from transporting materials and visitors to a new city every four years can be minimized. The timeframe for mitigating environmental damage shortens, as the commitment to sustainability becomes a consistent priority.
3. Cultural and Logistical Consistency
A single host city allows for a uniform and professional Olympic experience. Athletes, coaches, and spectators will become familiar with the city, leading to smoother operations and fewer logistical challenges. For example, transportation systems and lodging will be optimized for repeated use. While some argue that rotating hosts promotes cultural exchange, the Olympic Games themselves bring diverse cultures together through the athletes and spectators. The magnitude of cultural exposure remains high, but the risk of logistical issues—such as delayed construction or unprepared venues—drops significantly.
Sample Con Case
1. Global Cultural Exchange and Inclusion
Rotating the host city ensures that different countries have the opportunity to showcase their culture, heritage, and traditions to a global audience. For instance, Rio 2016 celebrated Brazil's vibrant culture. A permanent host city would concentrate cultural representation in one place, potentially leading to cultural homogenization. By moving the Games, the magnitude of global inclusion increases, promoting diversity and international understanding every four years.
2. Economic Opportunities for Host Cities
Hosting the Olympics can bring substantial economic benefits to the selected city, such as increased tourism, job creation, and global attention. For example, the 2012 London Olympics boosted tourism and revitalized the Stratford area. While hosting can be expensive, cities often use it as an opportunity for urban renewal and economic development. Limiting the Games to one city would concentrate these benefits in a single location, excluding many nations from these opportunities. The timeframe of these benefits might be shorter, but the impact can transform a city for decades.
3. Fairness and Equal Representation
The Olympics are meant to symbolize international unity and equality. Allowing different cities and countries to host the Games reflects these values. A single host city could lead to perceptions of favoritism, especially if that city is in a wealthy or influential nation. Rotating hosts ensures that countries from different regions and economic backgrounds have the chance to participate in this global event on equal footing. The risk of alienating less developed nations or those without the means to host permanently is minimized, preserving the inclusivity of the Olympic spirit.