在数学建模中主流的编程语言是MATLAB,但随着python/R中数学软件包的不断完善,熟悉这两种编程语言的同学也可以快速数学建模的编程环节。后面我们将介绍几种常见数学建模算法的python实现,旨在展示python在本领域的强大威力。
1、问题描述
你希望通过几种常见算法的实现,了解python在数学建模中的能力。
2、解决方案
python除了丰富的原生数据结构外,拥有强大的第三方软件包支持,例如矩阵运算库Numpy,数据处理库Pandas、机器学习库Sklearn、深度学习库Tenserflow&Pytorch、科学计算库Scipy、图形绘制库matplotlib、网络算法库Networkx。
此外几乎针对任何领域,都有第三方软件包的支持,这归功于python优秀的社区。使用者需要使用好pip这一软件包管理工具,发掘前人造好的轮子,尽量减少自己编程的难度。我们将在后面的问题讨论中介绍以下几种常用数学建模算法的python实现:
1.数据拟合算法
2.插值算法
3.线性规划算法
4.单源多宿最短路算法
3、问题讨论
我们的重点在于代码实现而非数学推导
1.数据拟合算法
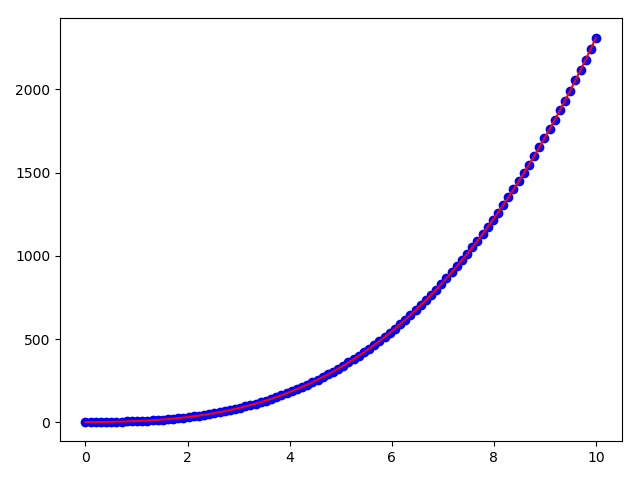
我们这里介绍通过最小二乘法拟合线性函数
#我们使用最小二乘法拟合一个三次函数,选取了5个参数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
SAMPLE_NUM = 100
M = 5
x = np.arange(0, SAMPLE_NUM).reshape(SAMPLE_NUM, 1) / (SAMPLE_NUM - 1) * 10
y = 2*x3+3*x2+x+1
plt.plot(x, y, 'bo')
X = x
for i in range(2, M + 1):
X = np.column_stack((X, pow(x, i)))
X = np.insert(X, 0, [1], 1)
W=np.linalg.inv((X.T.dot(X))).dot(X.T).dot(y)
y_estimate = X.dot(W)
plt.plot(x, y_estimate, 'r')
plt.show()
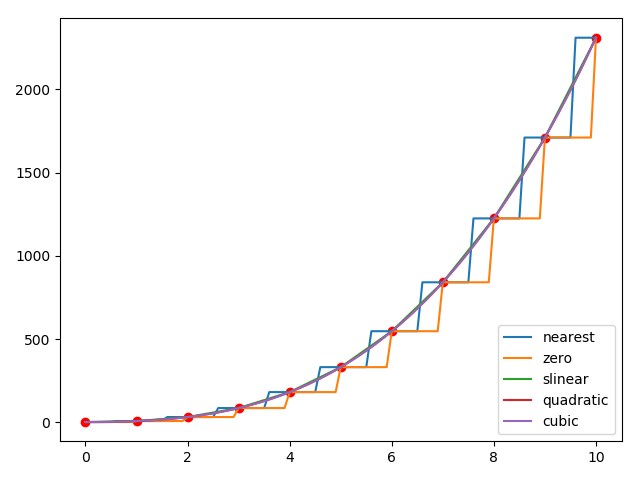
2.插值算法
我们使用几种常见的插值函数拟合上例中的三次函数
import numpy as np
from scipy import interpolate
import pylab as pl
x=np.linspace(0,10,11)
y=2*x3+3*x2+x+1
xInset=np.linspace(0,10,101)
pl.plot(x,y,"ro")
for kind in["nearest","zero","slinear","quadratic","cubic"]:
f=interpolate.interp1d(x,y,kind=kind)
y_estimate=f(xInset)
pl.plot(xInset,y_estimate,label=str(kind))
pl.legend(loc="lower right")
pl.show()
3.线性规划算法
我们可以使用scipy库对目标函数进行线性规划
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import minimize
def func(x):
return(2*x[0]*x[1]+2*x[0]-x[0]2+2*x[1]2+np.sin(x[0]))
cons=({"type":"eq","fun":lambda x:np.array([x[0]3-x[1]]),"jac":lambda x:np.array([3*(x[0]2),-1.0])},{"type":"ineq","fun":lambda x:np.array([x[1]-1]),"jac":lambda x:np.array([0,1])})#定义函数的多个约束条件
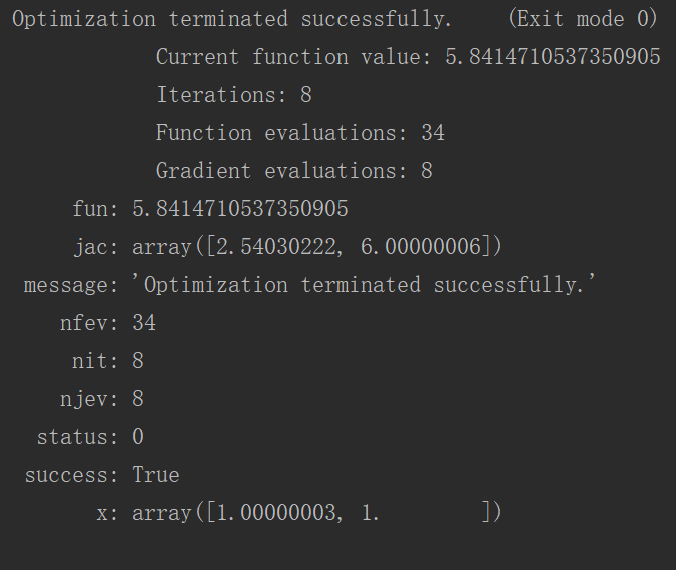
res=minimize(func,[-1.0,1.0],constraints=cons,method="SLSQP",options={"disp":True})
print(res)
注意这里求解的为目标函数最小值,如果我们需要求解最大值则将func取负数即可。输出内容如图
4.单源多宿最短路算法
我们介绍以下基于堆优化的dijkstra算法,这里的堆可以使用python内置的PriorityQueue实现。我们这里给出一个简单的堆实现:
classDisNode:
def __init__(self,node,dis):
self.node=node
self.dis=dis
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.dis<other.dis
classDisPath:
def __init__(self,end):
self.end=end
self.path=[self.end]
self.dis=0
def __str__(self):
nodes=self.path.copy()
return"->".join(list(map(str,nodes)))+" "+str(self.dis)
classHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.size=0
self.maxsize=10000
self.elements=[0]*(self.maxsize+1)
def isEmpty(self):
return self.size==0
def insert(self,value):
if self.isEmpty():
self.elements[1]=value
else:
index=self.size+1
while(index!=1and value<self.elements[index//2]):
self.elements[index]=self.elements[index//2]
index=index//2
self.elements[index]=value
self.size+=1
def pop(self):
deleteElement=self.elements[1]
self.elements[1]=self.elements[self.size]
self.size-=1
temp=self.elements[1]
parent,child=1,2
while(child<=self.size):
if child<self.size and self.elements[child]>self.elements[child+1]:
child+=1
if temp<self.elements[child]:
break
else:
self.elements[parent]=self.elements[child]
parent=child
child*=2
self.elements[parent]=temp
return deleteElement
defDijkstraWithHeap(nodes,start,GetNeighbors):
dis=defaultdict(int)
paths=defaultdict(DisPath)
heap=Heap()
visit=set()
for node in nodes:
dis[node]=sys.maxsize
paths[node]=DisPath(node)
dis[start]=0
heap.insert(DisNode(start,0))
while(not heap.isEmpty()):
now=heap.pop().node
if now in visit:
continue
visit.add(now)
paths[now].dis=dis[now]
for edge inGetNeighbors(now):
end=edge.End
if dis[now]+edge.value<dis[end]:
dis[end]=dis[now]+edge.value
paths[end].path=paths[now].path+[end]
heap.insert(DisNode(end,dis[end]))
return paths
通过堆优化的dijkstra算法的时间复杂度最低可以达到O(nlogm),上文给出的代码的时间复杂度为O(mlogm),但是胜在编码简单。此外还可以使用Networkx库进行求解,这里不再介绍。