最新变化
剑桥STEP 2021的官方更新
- 自2021年起取消STEP 1、仅保留STEP 2和STEP 3考试。
- 2021版STEP大纲内容与2020版一致,原STEP 1要求的知识点仍将在STEP 2和3中出现。
- STEP 2021考试相关日期已于3月8日公布。
- STEP 2021面向所有考生开放,没有offer的学生同样可以参加考试。
- 剑桥官方保留变更STEP 2021考试政策的权利。
关键日期
剑桥STEP 2021考试关键日期
| 2021年3月15日 | 注册报名开放 |
| 2021年5月07日 | 注册报名截止 |
| 2021年6月14日 | STEP 2考试日 |
| 2021年6月17日 | STEP 3考试日 |
| 2021年8月10日 | STEP成绩公布 |
注意:剑桥官方保留调整上述日期的权利。
特别提醒
STEP考试时间可能与A Level相关考试时间冲突,注意提前做好准备,如有时间冲突请务必提前做好相关考试科目的调整。报名方式剑桥STEP 2021考试如何报名?
考生需通过授权考试中心报名参加STEP考试:
- 考生所在学校是授权考试中心,则可通过学校报名和参加STEP考试。
- 学校不是授权考试中心,可以社会考生的身份登录BC官网报名。
- 还有部分城市有校外机构,可以代社会考生报名并组织STEP考试。
报名时需提交给考试中心以下信息:
- 姓名、性别、出生日期及UCAS编号。
- 所申请大学的名称、专业及专业代码。
- 如因身体原因需要特殊照顾,需一并提交相关证明材料。
报名资格
哪些学生可以报考STEP 2021?
所有人均可报名参加STEP 2021考试。不再像2020年那样要求必须是offer holder才能参加。 考试简介
考试简介
什么是剑桥STEP数学考试?由剑桥大学招生考试委员会组织的STEP考试是为测试申请者数学能力而举行的笔试,其全称为Sixth Term Examination Paper,直译过来就是“第六学期考试”。STEP成绩通常作为英国几所顶尖高等院校,包括剑桥大学、帝国理工学院、伦敦大学学院、华威大学等院校的数学、计算机等相关专业录取条件之一。尽管牛津大学数学、计算机相关专业不要求提供STEP成绩,但牛津官网上也明确建议申请者参加STEP考试。
需考专业哪些大学和专业需要考剑桥STEP?
剑桥大学
| Courses | 专业名称 | UCAS代码 |
| Mathematics | 数学 | G100 |
| Mathematics with Physics | 数学物理 | G100 |
| Economics | 经济 | L100 |
| Engineering | 工程 | H100 |
通常剑桥大学在条件录取中要求考生的STEP成绩达到等级1及以上。其中,数学专业通常要求STEP 2、3等级1、1甚至等级1、S的成绩。自2018年起剑桥大学以下专业不再要求考STEP:
- 化学工程 Chemical Engineering via Engineering (H810),但要求考ENGAA。
- 自然科学 Natural Sciences (BCF0),但要求考NSAA。
自2019年起剑桥大学以下专业不再要求考STEP:
- 计算机 Computer Science with Mathematics (G400 BA/CS),但要求考CTMUA。
华威大学
| Courses | 专业名称 | UCAS代码 |
| Mathematics | 数学 | G100 |
| Mathematics (Master of MATH) | 数学(四年) | G103 |
| Mathematics and Philosophy | 数学和哲学 | GV15 |
| Mathematics andStatistics | 数学与统计 | GG13 |
| Mathematics and Statistics (MMathStat) | 数学和统计(四年) | GGC3 |
| MORSE (Mathematics, Operational Research, Statistics and Economics) | 数学运筹学统计与经济(四年) | G0L0 |
| MORSE(Mathematics, Operational Research, Statistics andEconomics) | 数学运筹学统计与经济 | GLN0 |
| Data Science (Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science) | 数据科学 | G103 |
一般华威大学要求STEP成绩达到等级2及以上。尽管华威大学接受考生用MAT或TMUA代替STEP成绩,但很多考生因为各种原因错过每年10月底或11月初的MAT和TMUA考试,不得不选择参加次年6月的STEP考试。华威大学官方给出的TMUA最低要求为6.5(满分9.0分),而MAT因为每年成绩会有所变化,无法在考试成绩统计结果出来以前给出MAT对应的最低分数。自2018年起华威大学以下专业不再要求考STEP:数学与商学 Mathematics and Business Studies (G1NC)数学与经济学 Mathematics and Economics (GL11)
帝国理工
| Courses | 专业名称 | UCAS代码 |
| Computing | 计算 | G400 |
| Computing | 计算 | G401 |
| Computing(International Programme of Study) | 计算(国际项目) | G402 |
| Computing (Management and Finance) | 计算(管理和金融) | G501 |
| Computing(Software Engineering) | 计算(软件工程) | G600 |
| Computing(Security and Reliability) | 计算(安全和可靠性) | G610 |
| Computing(Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning) | 计算(人工智能和机器学习) | G700 |
| Computing(Visual Computing and Robotics) | 计算(视觉计算和机器人) | GG47 |
| Mathematics and Computer Science | 数学与计算机科学 | GG14 |
| Mathematics and Computer Science | 数学与计算机科学 | GG41 |
一般帝国理工在条件录取中要求STEP 2或3达到等级2或1以上,或者STEP 2和3同时达到等级2甚至等级1以上。
其他大学其他要求STEP(或MAT、TMUA)的大学包括:
- 伦敦大学学院(UCL)
- 布里斯托大学
- 巴斯大学
- 伦敦国王学院
上述大学的相关专业会在官网或录取条件中明确提出具体STEP考试和成绩等级要求。帝国理工的计算机专业必须要STEP,而数学专业通常要求MAT,如果没有MAT成绩则可以用STEP替代。通常帝国理工要求STEP 2或3等级2以上的成绩。牛津大学的数学、计算机等相关专业则要求考生必须参加自家组织的MAT(Mathematics Admissions Test数学入学考试)。尽管STEP成绩不作为牛津大学录取的必要条件之一,但牛津也鼓励考生参STEP考试并提供成绩,以全面评估考生的学术能力。
考试形式
剑桥STEP考试形式是怎样的?
考试题型
自2021年起取消STEP 1考试后,STEP仅提供STEP 2和STEP 3两种考试。
题型均为计算题,不必做答所有题目,考生只需从试卷中选择6道题作答。
自2019年改革以后,STEP 2和3试卷题量由13道减少为12道,见下表。
| 考试 | Section A | Section B | Section C | 合计 |
| STEP 2 | 纯数8道 | 力学2道 | 统计2道 | 12道 |
| STEP 3 | 纯数8道 | 力学2道 | 统计2道 | 12道 |
答题方式笔试
考试时长3小时
公式表考试不提供公式表,大纲中涉及的公式要求学生全部掌握,如果有超过大纲给出的公式,试题中会给出。
计算器不允许使用计算器词典
允许使用纸质双语词典
试卷样题
剑桥STEP试卷样以下为2020年STEP 2真题:Section A: Pure Mathematics
[STEP 2, 2020Q1]
(i) Use the substitution ,where , to find in terms of the integral
(where ).
(ii) Find in terms of the integral (where ).
(iii) Show that
[STEP 2, 2020Q2]
The curves and both satisfy the differential equation,
where .
All points on have positive and co-ordinates and passes through (1, 1). All points on have negative and co-ordinates and passes through (−1, −1).
(i) Show that the equation of can be written as .
Determine a similar result for curve .
Hence show that is a line of symmetry of each curve.
(ii) Sketch on the same axes the curves and , for . Hence show that lies between the lines and .
Sketch curve .
(iii) Sketch curve .
[STEP 2, 2020Q3]
A sequence of positive real numbers is said to be unimodal if there is a value such that
and
So the sequences ; ; and are all unimodal, but is not.
A sequence of positive real numbers is said to have property if for all with .
(i) Show that, in any sequence of positive real numbers with property L,
Prove that any sequence of positive real numbers with property is unimodal.
(ii) A sequence of real numbers satisfies for , where is a positive real constant. Prove that, for ,
and, for ,
Hence show that the sequence consists of positive terms and is unimodal, provided .
In the case and , prove by induction that . Let , where is an integer with .
In the case and , prove that ur is largest when .
[STEP 2, 2020Q4]
(i) Given that , and are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, explain why , and .
(ii) Use a diagram to show that the converse of the result in part (i) also holds: if , and are positive numbers such that , and then it is possible to construct a triangle with sides of length , and .
(iii) When , and are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, determine in each case whether the following sets of three lengths can
- always
- sometimes but not always
- never
form the sides of a triangle. Prove your claims.
(A) , , .
(B) , , .
(C) , , .
(D) , , .
(iv) Let f be a function defined on the positive real numbers and such that, whenever ,
but .
Show that, whenever , and are the lengths of the sides of a triangle, then , and can also be the lengths of the sides of a triangle.
[STEP 2, 2020Q5]
If is a positive integer, the value of the function is the sum of the digits of in base 10. For example, d(249) = 2 + 4 + 9 = 15.
An -digit positive integer is written in the form , where for all and .
(i) Prove that is non-negative and divisible by 9.
(ii) Prove that is a multiple of 9 if and only if is a multiple of 9.
Suppose that . Show that if has n digits, then and , and hence that .
Find a value of for which . Show that there are no further values of satisfying this equation.
(iii) Find a value of for which . Show that there are no further values of satisfying this equation.
[STEP 2, 2020Q6]
A matrix is real if it can be written as , where , , and are real.
In this case, the trace of matrix is defined to be tr and det() is the determinant of matrix . In this question, is a real 2 × 2 matrix.
(i) Prove that
tr() = tr − 2det().
(ii) Prove that
but and
and that
and
(iii) Use part (ii) to prove that
Find a necessary and sufficient condition on and so that .
(iv) Give an example of a matrix for which , but which does not represent a rotation or reflection. [Note that the matrices are both rotations.]
[STEP 2, 2020Q7]
In this question, .
(i) Let be the complex number , where . Show that is independent of . Hence show that, if is a complex number on the line in the Argand diagram, then lies on a circle in the Argand diagram with centre 1.
Let be the line , where is a real constant not equal to 2. Show that, if lies on , then lies on a circle whose centre and radius you should give in terms of . For which on is ?
(ii) Let be the line , where is a non-zero real constant. Show that, if lies on H, then lies on a circle whose centre and radius you should give in terms of . For which on is ?
[STEP 2, 2020Q8]
In this question, is a quartic polynomial where the coefficient of is equal to 1, and which has four real roots, 0, , and , where .
is defined by .
The area enclosed by the curve and the -axis between 0 and is equal to that between and , and half that between and .
(i) Sketch the curve , showing the co-ordinates of its turning points. Explain why must have the form , where . Find, in factorised form, an expression for in terms of , and .
(ii) If , explain why and why if . Hence show that or .
By considering also , show that and that .
(iii) Find an expression for in terms of and only. Show that the points of inflection on lie on the -axis.
Section B: Mechanics
[STEP 2, 2020Q9]
Point is a distance above ground level and point is directly below at ground level. Point is also at ground level, a distance horizontally from . The angle of elevation of from is . A particle is projected horizontally from , with initial speed . A second particle is projected from B with speed at an acute angle above the horizontal. The horizontal components of the velocities of the two particles are in opposite directions. The two particles are projected simultaneously, in the vertical plane through , and .
Given that the two particles collide, show that
and also that
(i) ;
(ii) ;
(iii) .
Show that the particles collide at a height greater than if and only if the particle projected from is moving upwards at the time of collision.
[STEP 2, 2020Q10]
A particle of mass m moves freely and without friction on a wire circle of radius , whose axis is horizontal. The highest point of the circle is , the lowest point of the circle is and angle . A light spring of modulus of elasticity λ is attached to and to . The natural length of the spring is , which is less than the diameter of the circle.
(i) Show that, if there is an equilibrium position of the particle at , where , then
Show also that there will only be such an equilibrium position if .
When the particle is at the lowest point of the circular wire, it has speed .
(ii) Show that, if the particle comes to rest before reaching , it does so when , where satisfies
where
Show also that this will only occur if .
Section C: Probability and Statistics
[STEP 2, 2020Q11]
A coin is tossed repeatedly. The probability that a head appears is and the probability that a tail appears is .
(i) A and B play a game. The game ends if two successive heads appear, in which case A wins, or if two successive tails appear, in which case B wins.
Show that the probability that the game never ends is 0.
Given that the first toss is a head, show that the probability that A wins is .
Find and simplify an expression for the probability that A wins.
(ii) A and B play another game. The game ends if three successive heads appear, in which case A wins, or if three successive tails appear, in which case B wins.
Show that
P(A wins | the first toss is a head) = P(A wins | the first toss is a tail) and give a similar result for P(A wins | the first toss is a tail).
Show that
P(A wins) =
(ii) A and B play a third game. The game ends if a successive heads appear, in which case A wins, or if successive tails appear, in which case B wins, where and are integers greater than 1.
Find the probability that A wins this game.
Verify that your result agrees with part (i) when .
[STEP 2, 2020Q12]
The score shown on a biased -sided die is represented by the random variable which has distribution for , where not all the are equal to 0.
(i) Find the probability that, when the die is rolled twice, the same score is shown on both rolls. Hence determine whether it is more likely for a fair die or a biased die to show the same score on two successive rolls.
(ii) Use part (i) to prove that, for any set of positive numbers ,
(ii) Determine, with justification, whether it is more likely for a fair die or a biased die to show the same score on three successive rolls.
计分方式
剑桥STEP考试计分方式是怎样的?
STEP考试计分方式
考生作答6道题,每题均为20分,全卷满分120分。尽管只需要做6道题,但不限制考生的答题数量。考生答题超过6道时,每道题都会判分,但只取得分最高的6道题计入总分。需要注意的是STEP计分采用鼓励性原则:STEP强调考生能在解题过程中完整做答,如果使用的解题方法非常巧妙、且答题过程完整,考官会酌情给出bonus mark。也即有考生一道题能得分超过20分!
STEP考试成绩等级
| 等级 | 含义 | 占比 |
| S | Outstanding (优秀) | 约前5~15% |
| 1 | Very Good (非常好) | 约前15~30% |
| 2 | Good (好) | 约前30~50% |
| 3 | Satisfactory (合格) | 约前50~80% |
| U | Unclassified (不合格) | _ |
需要注意的是,尽管STEP 2、3的满分、等级都一样,但每种考试每年各个等级对应的分数阈值都不一样。
STEP考试成绩等级划分标准
以下为2020年官方给出的STEP 2和3的等级划分标准和统计图。
STEP 2等级划分标准和统计图Grade boudaries (STEP 2, 2020)等级划分标准
| Maximum Mark | S | 1 | 2 | 3 | U |
| 120 | 77 | 55 | 42 | 25 | 0 |
Cumulative percentage achieving each grade (STEP 2, 2020)达到各等级的累积百分比
| Maximum Mark | S | 1 | 2 | 3 | U |
| 120 | 9.3 | 30.8 | 48.4 | 81.3 | 100 |
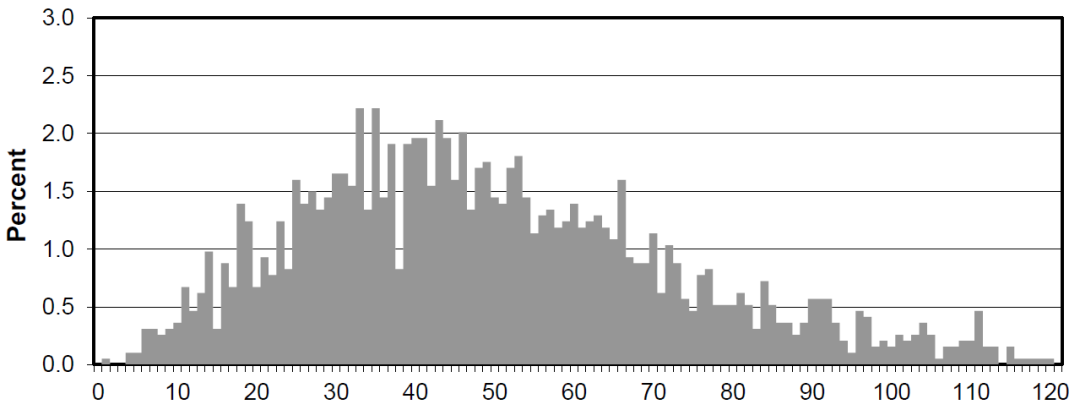
Distribution of scores (STEP 2, 2020)分数分布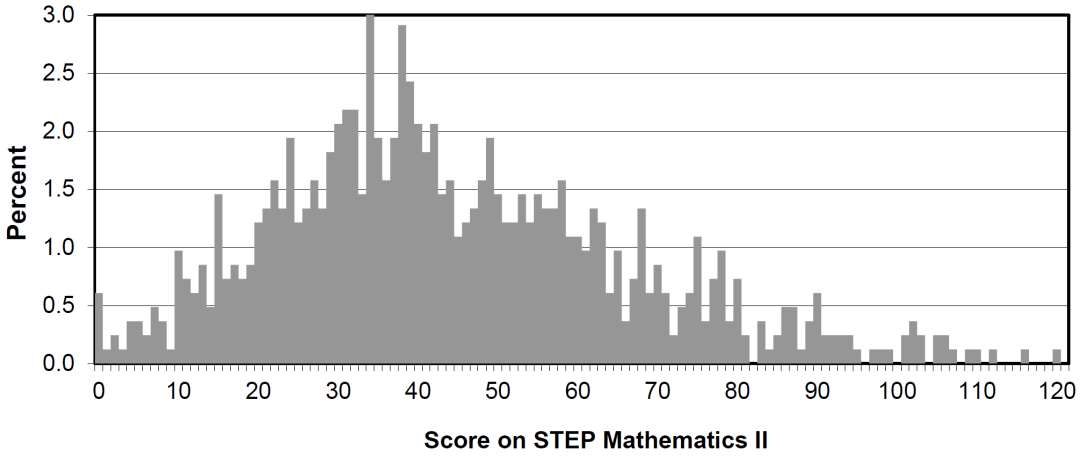 STEP 3等级划分标准和统计图Grade boudaries (STEP 3, 2020)等级划分标准
STEP 3等级划分标准和统计图Grade boudaries (STEP 3, 2020)等级划分标准
| Maximum Mark | S | 1 | 2 | 3 | U |
| 120 | 80 | 67 | 53 | 30 | 0 |
Cumulative percentage achieving each grade (STEP 3, 2020)达到各等级的累积百分比
| Maximum Mark | S | 1 | 2 | 3 | U |
| 120 | 11.6 | 38.2 | 58.3 | 83.5 | 100 |
Distribution of scores (STEP 3, 2020)分数分布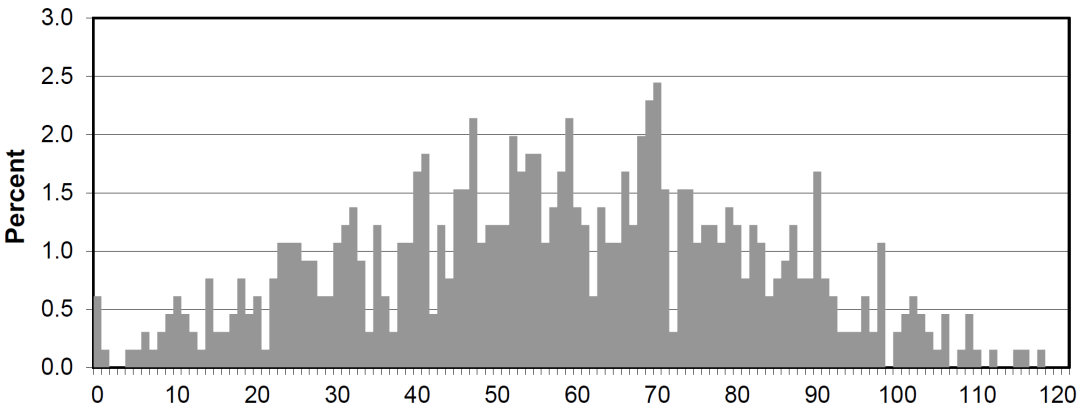 考试范围
考试范围
剑桥STEP考试范围有哪些变化?STEP考试的考查范围见下表。
| 考试 | 考察范围 |
| STEP 1(已取消,但仍作为STEP 2和3的知识点) | A Level数学的纯数、力学、概率统计部分,附加2021大纲要求的内容 |
| STEP 2(同样作为STEP 3的知识点) | AS进阶数学 (高数) 的纯数、力学、概率统计部分,附加2021大纲要求的内容 |
| STEP 3 | A level进阶数学(高数)的纯数、力学、概率统计部分,附加2021大纲要求的内容 |
为了适应近几年的A Level课程改革,STEP考试在2019年做了重大调整,最主要的变化是对STEP 2、3的考试范围和试卷结构进行了调整,但题型没有变化。主要变化简述如下:
- 按照A Level数学和进阶数学(高数)改革对应的修订考试大纲;
- STEP 2和3试卷的题量由13道减少为12道;
- 出题风格不变,意味着往年的STEP真题可以用于备考;
- 考试的鼓励性计分原则不变。
最新的2021年大纲已经出炉,与2020年的大纲相比几乎没有变化。
考试难度
剑桥STEP考试有多难?一句话概括难度STEP有少量题比较简单,但大多数题都是高考压轴题难度,尤其是每道题的最后一问非常有挑战性。
近几年STEP考试越来越难吗?
是的,经过牛剑课程教学和研发团队的对比分析,发现最近几年STEP试题难度有明显提升。一个明显的变化是划分等级S和等级1的分数线上有大幅下降的趋势,另一方面考虑到越来越多数学成绩优秀的中国学生参加STEP考试,无疑会在一定程度上提高各个等级的分数线。
STEP考试难在哪儿?
- 强调逻辑推理的完备性;
- 计算量大且不能用计算器;
- 要求基本数学运算相当熟练;
- 注重数学基本知识和基本定理、公式的推导方法所蕴含的基本数学思想;
- 通过已知与未知知识的并行使用考查学生的领悟能力和知识迁移能力。
STEP和数学竞赛相比哪个难?
- 试题难度:总体来说STEP的难度没有大多数数学竞赛最后几道题难;
- 侧重考查点:STEP更强调对基本数学知识、思想方法的运用,而数学竞赛强调巧思妙解、是对智商和数学技巧的双重考验;
- 答题策略:取决于题型,多数数学竞赛的初赛以选择题为主,相对于STEP所有的题都是解答题而言会更容易得分;
- 备考方式:STEP有考纲和明确的考试范围,题型和解答套路相对比较固定,所以更容易备考,而竞赛没有考纲、也没有明确的考试范围,有些难题不能按常规套路求解、不容易准备。
参加数学竞赛对考STEP有帮助吗?
虽然STEP和数学竞赛试题存在诸多差异,但在备考数学竞赛过程中学到的数学知识、方法和思想对于备考STEP考试也是非常有帮助的,建议学有余力的学生在备考STEP的同时参加数学竞赛,比如美国数学竞赛AMC 10/12、英国数学竞赛BMO系列赛事等。
MAT跟STEP相比难度如何?
MAT比STEP简单。MAT仅考查纯数知识,考查范围比原STEP 1考试的纯数部分考查的知识还要少。MAT有选择题,且选择题大部分都比较容易,通常只有2-3道选择题比较难或容易丢分。MAT考试这样设置的原因一方面是要兼顾申请帝国理工和华威大学的考生数学水平,另一方面也是为了不让考生的MAT成绩太难看,鼓励更多的学生参加MAT考试,并通过MAT考试测评其数学实力。
而STEP考试全是大题,且大题之间的难度差异比较大。所以STEP考试不全是考查数学水平,也不像考MAT的选择题会有一定的运气成分,STEP考试中会挑题比会解题更重要!题目挑得好就会更容易得高分。
STEP准备多久才能考到等级1以上?
不同学生的数学基础差别较大,剑桥官方建议备考STEP时间不少于6个月。没有学高数和数学竞赛基础的学生,建议备考时间9个月以上。
学过高数且有数学竞赛基础的学生如果准备STEP 2和3,建议不少于6个月。