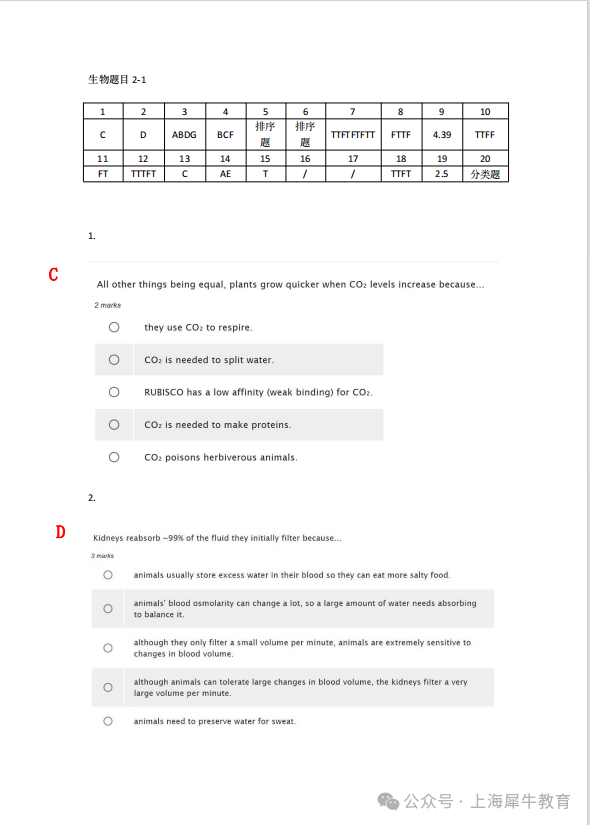
加拿大化学竞赛(Canadian Chemistry Contest)竞赛竟然考到四种分子间作用力?学alevel是不会告诉你的。一般alevel只学到三种分子间作用力:
而在CCC考纲明确要求我们需要掌握4种,并且能够利用这些分子间作用力判断熔沸点和溶解度。
5.11 explain the effect of solutes on the melting point of solid water, using intermolecular forces
根据我在《加拿大化学竞赛CCC复习指导》给大家总结的内容,跟大家补充一下这方面的知识:
Intermolecular forces的定义:
Intermolecular forces are attractive forces between molecules. They are largely responsible for the observed boiling points and solubility properties of molecules.

1. 伦敦力,也叫色散力:
1). London Dispersion: Attraction between molecules that form due to a temporary dipole on one molecule inducing a temporary dipole in neighboring molecules.
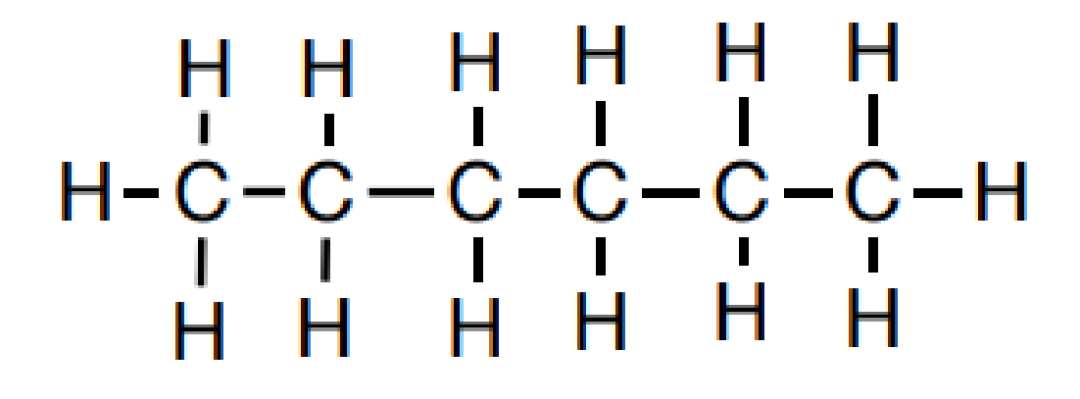
2.偶极-偶极 作用
2). Dipole-Dipole: Attraction between two polar molecules (dipoles)
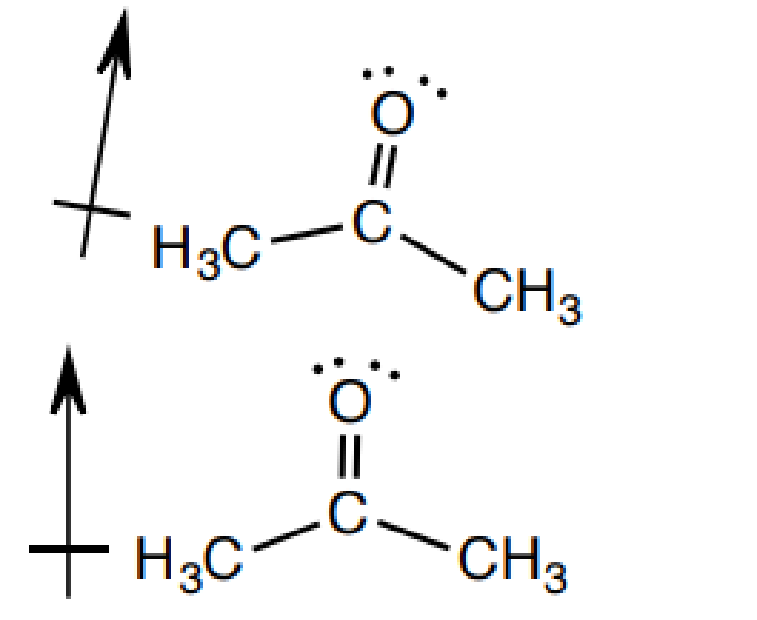
3. 氢键
3). Hydrogen Bonding: Attraction between two polar molecules, specifically one molecule having a H bonded directly to an electronegative atom (eg. H-O-, H-N-, HF), and the other having a non-bonding electron pair on an electronegative atom.
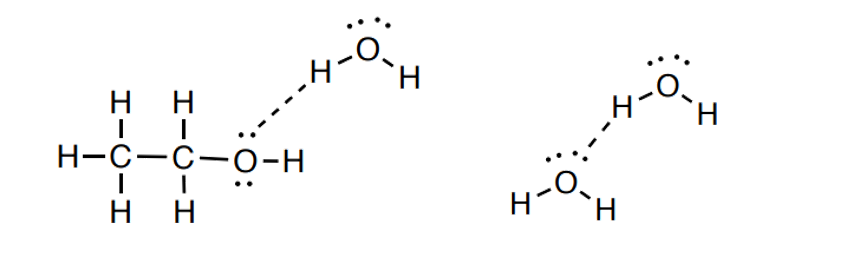
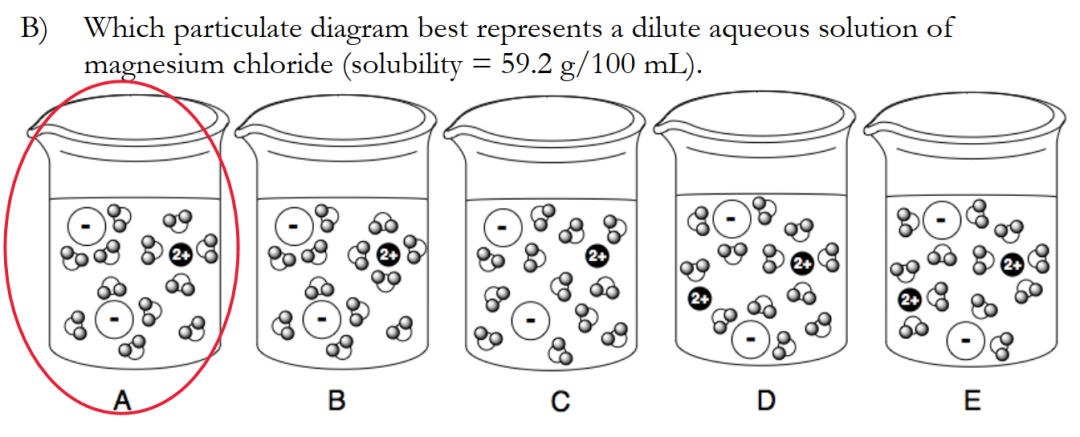
4. 离子偶极作用(这是我们今天提到的!)
4).Ion-Dipole: Attraction between an ion and a polar molecule.
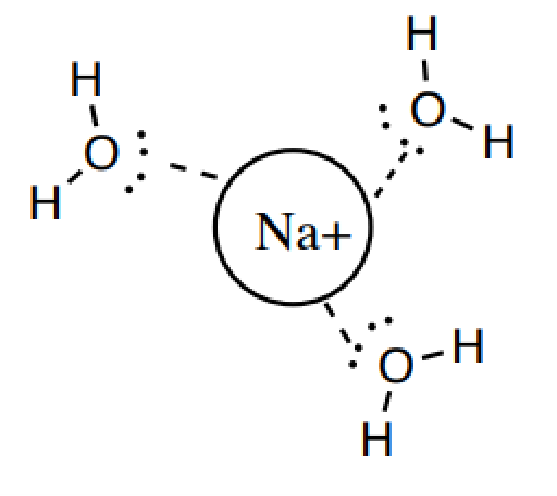
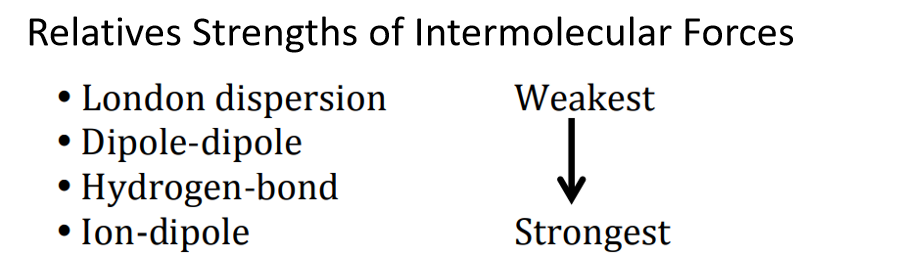
这几种力相对强弱如下:
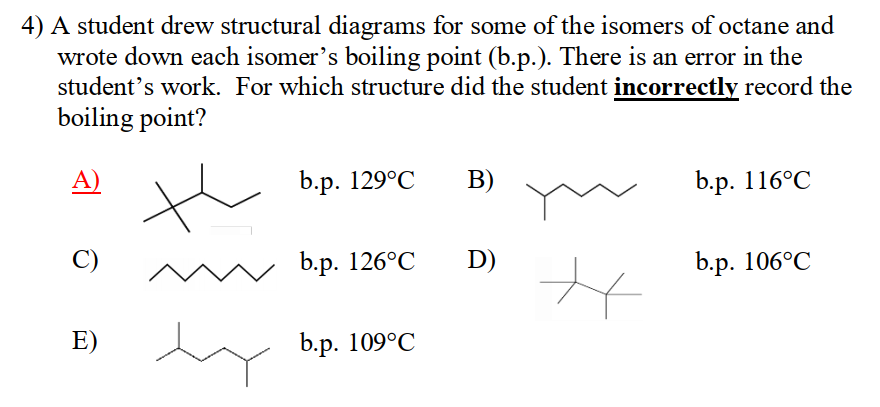
如果你需要判断他们熔沸点的大小,除了知道这些作用力还需要了解这些“趋势(trends)”:
-
Between two molecules of similar mass, the one with the stronger type of intermolecular force has a higher boiling point.

2. Between two nonpolar molecules of similar mass, the more extended molecule will have the higher boiling point (more extended amore surface area for London dispersion interaction).
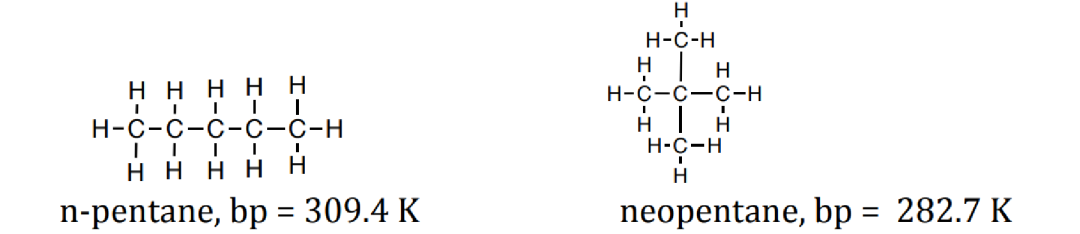
3. Between two nonpolar molecules of different masses, the larger molecule will have the higher boiling point (larger molecule → more electrons → more polarizability → more London dispersion forces)

相关真题我总结在《加拿大化学思维挑战CCC分类真题》专辑里面: