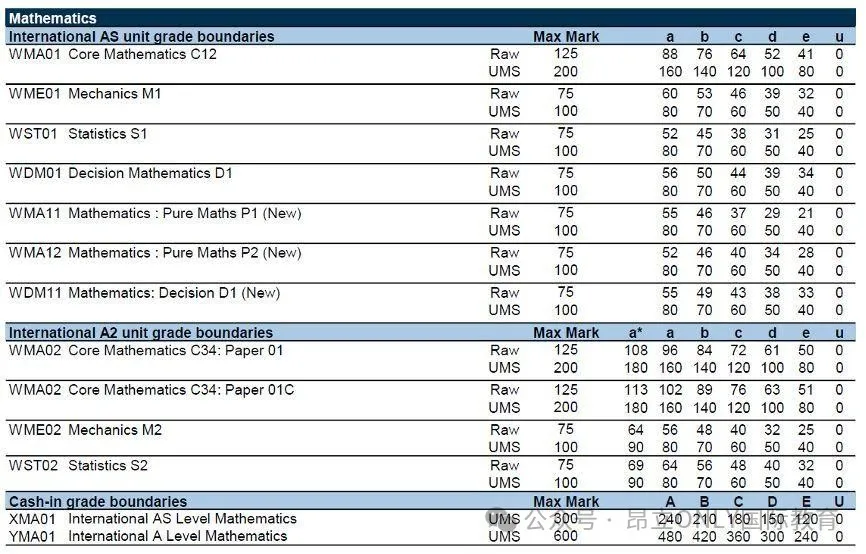
在本年的AMC10 B卷中,出现了一道背景较深刻的问题:

来看看机构的老师怎样带领我们破题:

Kayles Game
事实上,此问题是组合博弈论当中的一个经典问题:Kayles Game。它是Henry Dudeney在1908年发明的,最初是说击打保龄球,而Kayles的发音与法语“quilles”很接近,故后称为Kayles Game。Kayles Game与Nim很类似,Nim指的是两个玩家轮流从不同的堆 ( piles ) 取走或移除物体。
每一回合 ( round ) 每个玩家必须移走至少一个物体,并且可以移除任意数量的物体,只要它们来自一堆。
事实上,组合博弈论有一个非常重要的定理刻画了这种相似性,也即著名的Sprague-Grundy定理。它陈述:“Every impartial game under the normal play convention is equivalent to a one-heap game of Nim, or to an infinite generalization of Nim.”(其中impartial指player 1与player 2之间唯一区别是轮次,而normal play convention指拿走最后一个者判胜,one-heap指Nim中的一堆,在有限博弈中,大可以忽略infinite generation)。
使用Nim-value和Nim-sum的计算方法,我们可以递归地找到Kayles问题的Nim序列:

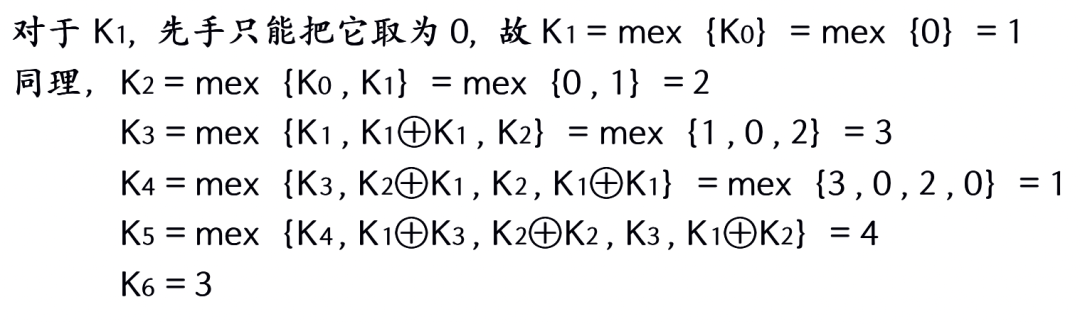
有了Nim-value,就可以知道所有Nim-sum非0的初始条件都是先手必胜,原因在于Kayles Game中若只有一堆砖头,先手可以造出镜像局面给后手从而不败。
而 ( B ) 中 ( 6 , 2 , 1 ) 的Nim-sum = 3 ⊕ 2 ⊕1 = 0
![]()
学会了Nim方法和Sprague-Grundy定理后,老师为大家留下了一道课后作业,来试试看求如下游戏的Nim值:
On a rectangular board, 2 players take turns placing dominoes either horizontally or vertically until no more dominoes (1×2) can be placed. The first player unable to make a move loses.
(Hint: 2×n board has a nimber of 0 for 2/n and nimber of 1 for 2+n)